If we want to make a list of the most common questions about Iranians, “Are Iranians Arabs?” would be at the top of the list. If you have an Iranian friend, you may witness people asking this question a lot from them. There are different reactions to this simple question. Some people laugh, some others get serious and want to explain, but we have seen a number of people who get mad when someone is asking them this question. We will talk about the reason behind this anger, but to those looking for a short answer, we can just say, “no, only 2 to 3 percent of Iranians are Arabs.”
We will take you on a historical, linguistic, and anthropological journey to find some interesting details that show how Iranians and Arabs are different. Before doing that, let’s read one of the best verses of Saadi’s that beautifully shows how unimportant your nationality is when you are a part of a bigger system:
Human beings are members of a whole
In creation of one essence and soul
Table of Contents
Why Do People Think Iranians Are Arabs?

We can search for the answer by looking at where Iran is located. But before that, let’s define the word Arab. According to the Cambridge Dictionary, Arabs are people who are “from Western Asia or North Africa who speaks Arabic as a first language.” Located in West Asia, somewhere in the heart of the Middle East, next to some Arabic countries such as Iraq (the similarity between the names of Iran and Iraq also makes people think there is a relation).
This geographical location is one of the main reasons for people to consider Iran an Arab country as well. Iranians also look like the stereotypes of what the majority think of Arabs because of having thick black hair and dark eyes. So, the people outside of the Middle East usually mistake them. It is very normal for people who live in the same geography to look similar because there is a long history behind them, and they can share similar genes.
Farsi writing and typography are also another main reason that makes people think Iranians are Arabs. Although the phonology of Persian is different from Arabic, Iran and Arabic countries have similar typography, which leads us to an exciting history lesson.
Iranians and Arabs in the History
Iranians and Arabs were always neighbors, but their most important encounter would be when the Arab Army marched toward Iran and conquered this country some time from 633 to 654 AD. Iran was not the only country that the Arab army defeated. Iraq, Lebanon, some European countries, and even Egypt are among those countries which Arabs successfully conquered to introduce the new religion. Islam was a new religion born in Western Arabia; these conquests introduced this religion to other people. Although it took many years, Arabic culture and language got combined with the native language of those countries.
This was not the only time that Arabic culture found its way to the Middle East. Later, during the Ottoman Empire, which was one of the most powerful empires in the world, Arabic culture dominated some important parts of Asia, Africa, and Europe. These two historical events have had significant impacts on the culture of many countries, from Afghanistan to Algeria. As you can see today, most of these countries have Arabic-speaking people even though they were not always Arabic.
However, this impact on Iran was not precisely the same.
Religion: A Key Factor
When it comes to determining if a country is an Arab country or not, religion plays a significant role. Almost all Arab countries are Muslims, but all Muslim countries are not Arab. Doesn’t it sound complicated?
Religion is a huge part of a nationality’s culture. People’s beliefs can make them change their lifestyle, language and eventually build traditions. Although this pattern happened in Iran, its effect was not the same as in other countries such as Iraq. Iranians believed in Zoroastrianism for a long time. The prophet, Zoroaster, was born in Iran and introduced this belief first to Iranians.
As a part of Iran, Iraq, and other countries had branches of Zoroastrianism as their religion. However, when Islam came, all the national events changed to Islamic ones. Although the formal religion of Iran is Islam, the main events have remained as they were years ago, during Zoroastrianism. So, unlike Arabic countries, Iranians celebrate the new year during Nowruz, not the Islamic new year that happens in December.
Also, almost the majority of Arabs are Sunni which is a branch of Islam, while Iranian Muslims are Shia, another Islamic branch.
Do Iranians Speak Arabic?

No, Iranians do not speak Arabic, but the Arabic culture entered Iran many years ago, so the combination of Persian and Arab, especially in language, was inevitable. When Islam entered Iran and got accepted as the main religion of that time’s government, Iran’s official language also changed to Arabic.
Although Iranians spoke their language, which was Persian, they had to know Arabic, especially for writing to be able to take care of their needs when it came to doing paperwork. ٍٍEventually, many Arabic words entered Persian and stayed in this language. If we look at this process from a linguistic point of view, we realize that language is dynamic, and it is very normal to see a language adopt new words. However, Persian and Arabic are fundamentally different.
What Are the Differences between Persian and Arabic?
We can look at different parts of a language to see how different Persian and Arabic are. The first one is their root.
Root and Language Family
If we draw a map of different languages in the world, we get to some important categories that are the roots of all languages. For Persian, this line goes to the Indo-European language family. Languages like Dutch, French, and Spanish are the descendants of this family.
On the other hand, Arabic comes from a totally different family called Afroasiatic, which is also the root of many African languages.
Both of these languages are truly beautiful, but now you can see how Persian and Arabic are different in nature.
Grammar
One of the most important parts of a language is its grammar, right? You should know that Persian is totally different from Arabic grammatically as well. Let’s see how.
Word Order
When it comes to making a sentence, Arabic has a similar word order to English. So, you see “Subject – Verb – Object” while Persian, aka Farsi, is totally different. In Persian, you need to follow the SOV order which is “Subject – Object – Verb”.
Gender
There are many languages that categorise different elements on a “gender-based” rule, like English and, of course, French. Arabic is also the same! You can put nouns and adjectives in two different masculine and feminine categories by following a pattern. However, in Persian, there is no difference between masculine and feminine words, and this is why the Persian language is one of the most gender-neutral languages in the world.
Plural
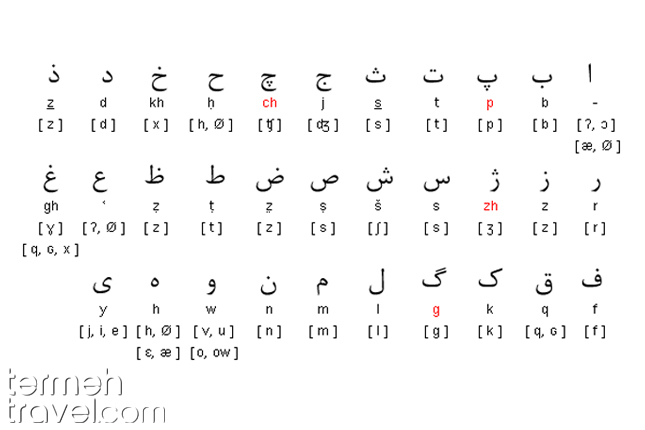
Another big difference between Persian and Arabic grammar is plural rules. In Arabic, you need to follow certain rules and add a few letters to the end of a word, while making a word plural is much easier in Farsi. However, the Arabic words that entered the Persian language follow the Arabic plural rules.
Although nationality is one of the least important things in today’s world, especially when we have zero control over choosing it, you now know that Iranians are not Arabs. If you want to know more about Iran, you should start reading our Persian language guide and get to know this amazing country by checking out other blog posts about Iranian culture.









Leave a Comment